Lifespan changes: From wild type to daf-16;utx-1
20
HT115
9.89
-39.44%
While utx-1 RNAi effectively extended the life span of wild-type N2 strain, such an effect could not be observed in any mutant on IIS pathway; utx-1 RNAi could not further increase the life span of daf-2(e1370) worms and could not at all increase the life span in daf-16(mu86) mutant animals.
Double mutant daf-16(mu86);utx-1(RNAi) has a lifespan of 9.89 days, while single mutant utx-1(RNAi) has a lifespan of 19.06 days, single mutant daf-16(mu86) has a lifespan of 11.08 days and wild type has a lifespan of 16.33 days.
Enhancer, opposite lifespan effects
Jin C et al., 2011, Histone demethylase UTX-1 regulates C. elegans life span by targeting the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway. Cell Metab. 14(2):161-72 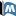 21803287
Click here to select all mutants from this PubMed ID in the graph
21803287
Click here to select all mutants from this PubMed ID in the graph
20
HT115
10.4
-35.64%
While utx-1 RNAi effectively extended the life span of wild-type N2 strain, such an effect could not be observed in any mutant on IIS pathway; utx-1 RNAi could not further increase the life span of daf-2(e1370) worms and could not at all increase the life span in daf-16(mu86) mutant animals.
Double mutant daf-16(mu86);utx-1(RNAi) has a lifespan of 10.4 days, while single mutant utx-1(RNAi) has a lifespan of 19.18 days, single mutant daf-16(mu86) has a lifespan of 11.05 days and wild type has a lifespan of 16.16 days.
Opposite lifespan effects of single mutants
Jin C et al., 2011, Histone demethylase UTX-1 regulates C. elegans life span by targeting the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway. Cell Metab. 14(2):161-72 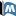 21803287
Click here to select all mutants from this PubMed ID in the graph
21803287
Click here to select all mutants from this PubMed ID in the graph
20
HT115
9.1
-43.97%
While utx-1 RNAi effectively extended the life span of wild-type N2 strain, such an effect could not be observed in any mutant on IIS pathway; utx-1 RNAi could not further increase the life span of daf-2(e1370) worms and could not at all increase the life span in daf-16(mu86) mutant animals.
Double mutant daf-16(mu86);utx-1(RNAi) has a lifespan of 9.1 days, while single mutant utx-1(RNAi) has a lifespan of 19.07 days, single mutant daf-16(mu86) has a lifespan of 9.98 days and wild type has a lifespan of 16.24 days.
Opposite lifespan effects of single mutants
Jin C et al., 2011, Histone demethylase UTX-1 regulates C. elegans life span by targeting the insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway. Cell Metab. 14(2):161-72 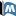 21803287
Click here to select all mutants from this PubMed ID in the graph
21803287
Click here to select all mutants from this PubMed ID in the graph
25
NGM
17.33
-8.79%
While utx-1 knockdown significantly extended the lifespan of wild type (N2) worms, utx-1 knock-down no longer extended the lifespan of the daf-16(mu86) mutant worms.
Double mutant daf-16(mu86);utx-1(RNAi) has a lifespan of 17.33 days, while single mutant utx-1(RNAi) has a lifespan of 24.66 days, single mutant daf-16(mu86) has a lifespan of 15.0 days and wild type has a lifespan of 19.0 days.
Opposite lifespan effects of single mutants
Maures TJ et al., 2011, The H3K27 demethylase UTX-1 regulates C. elegans lifespan in a germline-independent, insulin-dependent manner. Aging Cell. 10(6):980-90 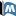 21834846
Click here to select all mutants from this PubMed ID in the graph
21834846
Click here to select all mutants from this PubMed ID in the graph
25
NGM
16.42
-16.31%
While utx-1 knockdown significantly extended the lifespan of wild type (N2) worms, utx-1 knock-down no longer extended the lifespan of the daf-16(mu86) mutant worms.
Double mutant daf-16(mu86);utx-1(RNAi) has a lifespan of 16.42 days, while single mutant utx-1(RNAi) has a lifespan of 25.16 days, single mutant daf-16(mu86) has a lifespan of 15.59 days and wild type has a lifespan of 19.62 days.
Opposite lifespan effects of single mutants
Maures TJ et al., 2011, The H3K27 demethylase UTX-1 regulates C. elegans lifespan in a germline-independent, insulin-dependent manner. Aging Cell. 10(6):980-90  21834846
Click here to select all mutants from this PubMed ID in the graph
21834846
Click here to select all mutants from this PubMed ID in the graph
Forkhead box protein O;hypothetical protein
Locus: CELE_R13H8.1
Wormbase description: daf-16 encodes the sole C. elegans forkhead box O (FOXO) homologue; DAF-16 functions as a transcription factor that acts in the insulin/IGF-1-mediated signaling (IIS) pathway that regulates dauer formation, longevity, fat metabolism, stress response, and innate immunity; DAF-16 regulates these various processes through isoform-specific expression, isoform-specific regulation by different AKT kinases, and differential regulation of target genes; DAF-16 can interact with the CBP-1 transcription cofactor in vitro, and interacts genetically with other genes in the insulin signaling and with daf-12, which encodes a nuclear hormone receptor; DAF-16 is activated in response to DNA damage during development and co-regulated by EGL-27, alleviates DNA-damage-induced developmental arrest by inducing DAF-16-associated element (DAE)-regulated genes; DAF-16 is broadly expressed but displays isoform-specific tissue enrichment; DAF-16 localizes to both the cytoplasm and the nucleus, with the ratio between the two an important regulator of function.
human UTX (Ubiquitously transcribed TPR on X) homolog
Locus: CELE_D2021.1
Wormbase description: utx-1 encodes a putative histone H3 di/trimethyllysine-27 (H3K27me2/me3) demethylase, required for embryonic viability and vulval development, and for high brood sizes, locomotion, and growth sizes; UTX-1 contains a JmjC domain, is orthologous to human UTX and UTY, and is paralogous to human JMJD3; by orthology, UTX-1 is expected to antagonize transcriptional repression by polycomb repressor complexes, which mark stem cells (and presumably germline) by H3K27me3-mediated repression of somatic genes.
| Show in SynergyAge | |
|---|---|
| Species | Gene |
| Show in SynergyAge | |
|---|---|
| Species | Gene |
| Show in SynergyAge | |
|---|---|
| Species | Gene |
SynergyAge database hosts high-quality, manually curated information about the synergistic and antagonistic lifespan effects of genetic interventions in model organisms, also allowing users to explore the longevity relationships between genes in a visual way.
If you would like to cite this database please use:
Bunu, G., Toren, D., Ion, C. et al. SynergyAge, a curated database for synergistic and antagonistic interactions of longevity-associated genes. Sci Data 7, 366 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-020-00710-z
Group webpage: www.aging-research.group